Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market (2025-2031) | Competitive Landscape, Forecast, Growth, Trends, Share, Companies, Segmentation, Value, Size & Revenue, Analysis, Industry, Outlook
| Product Code: ETC7913508 | Publication Date: Sep 2024 | Updated Date: Nov 2025 | Product Type: Market Research Report | |
| Publisher: 6Wresearch | Author: Summon Dutta | No. of Pages: 75 | No. of Figures: 35 | No. of Tables: 20 |
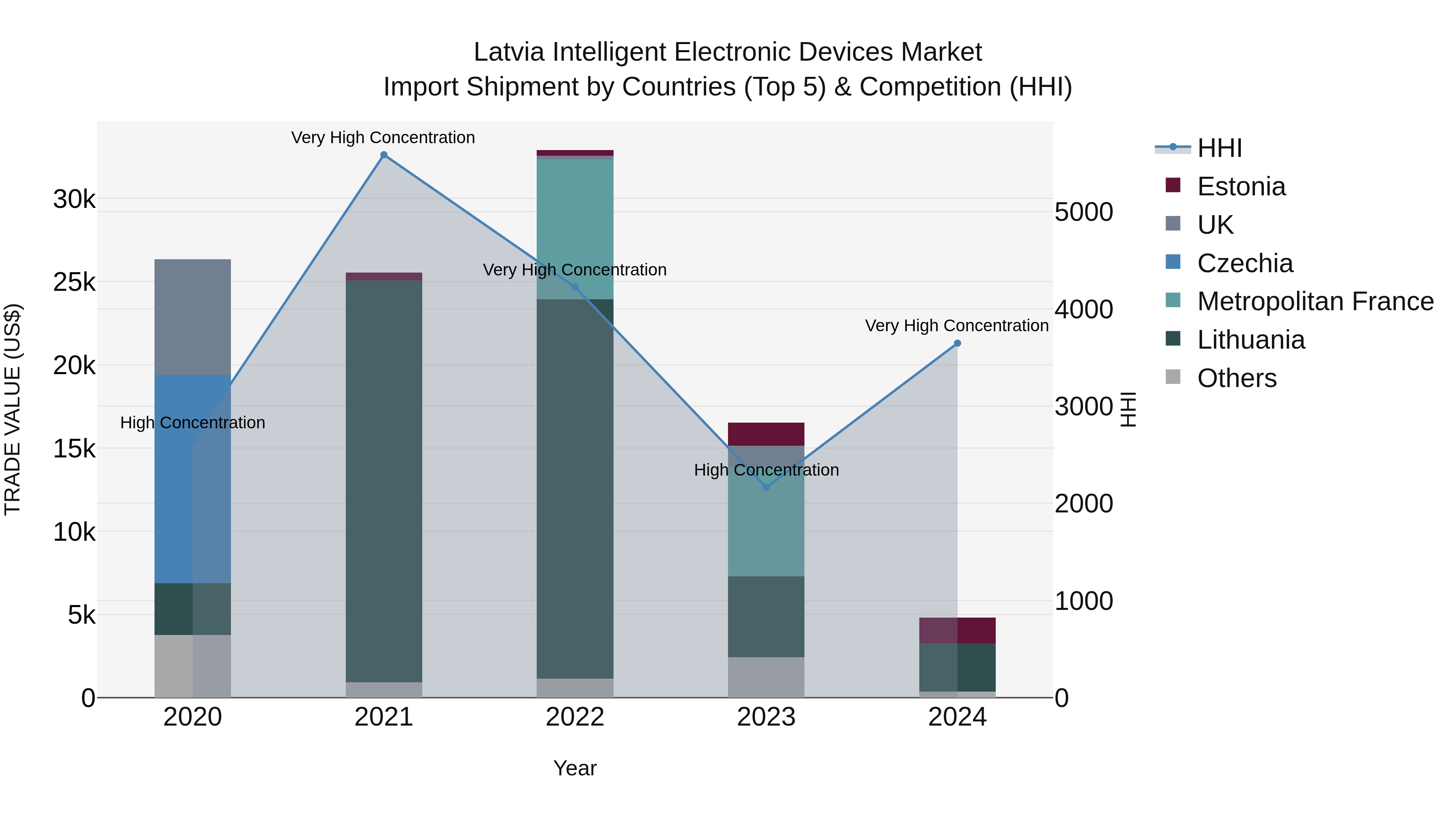
Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Top 5 Importing Countries and Market Competition (HHI) Analysis
Despite a decline in the growth rate of intelligent electronic device imports to Latvia in 2024, the market continues to see high concentration among the top exporting countries, with Lithuania, Estonia, USA, China, and Italy leading the pack. The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) indicates a significant increase in market concentration, which may have implications for competition and pricing dynamics. The negative CAGR from 2020 to 2024 suggests a challenging market environment, underscoring the need for strategic adaptation and potentially new market entrants to drive innovation and competitiveness in the sector.
Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Synopsis
The Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) market is experiencing steady growth driven by the increasing adoption of smart technologies across various industries. The demand for IEDs such as smart meters, relays, and sensors is rising as businesses and consumers seek to improve energy efficiency, enhance automation, and ensure reliable operations. Key market players are focusing on developing advanced IEDs with features like real-time monitoring, data analytics capabilities, and seamless integration with existing systems. Government initiatives promoting digitalization and energy efficiency are further fueling market growth. The Latvia IEDs market is characterized by intense competition, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. As businesses continue to digitize and modernize their operations, the demand for intelligent electronic devices is expected to increase, presenting opportunities for market expansion and innovation.
Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Trends
The Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED) market is experiencing growth due to increasing demand for smart technologies in various industries such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation. Key trends include the adoption of IoT devices for improved connectivity and data collection, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for enhanced decision-making capabilities, and the focus on cybersecurity to protect sensitive information. Opportunities in the market lie in the development of advanced IED solutions tailored to specific industry needs, partnerships with local businesses to expand market reach, and investment in research and development to stay ahead in the competitive landscape. Overall, the Latvia IED market presents promising prospects for companies looking to innovate and capitalize on the growing demand for intelligent electronic devices.
Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Challenges
In the Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED) market, one of the key challenges faced is the relatively small size of the market compared to larger countries, which can limit the opportunities for growth and scale. Additionally, the high cost associated with implementing IED solutions and the limited awareness among businesses about the benefits of these technologies can hinder adoption rates. Regulatory barriers and interoperability issues between different IED systems can also pose challenges for market players. Furthermore, the lack of skilled professionals with expertise in IED technologies and cybersecurity concerns are additional obstacles that need to be addressed to drive further development and innovation in the Latvia IED market.
Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Investment Opportunities
The Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market is primarily driven by the increasing demand for smart grid technologies to improve energy efficiency and reliability in the country. The growing integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, is also fueling the adoption of intelligent electronic devices to manage the grid effectively. Additionally, government initiatives and investments in modernizing the power infrastructure are driving the market growth. The need for real-time monitoring and control of power systems, along with the rising focus on grid modernization and automation, are key factors propelling the demand for intelligent electronic devices in Latvia. Moreover, the increasing awareness about the benefits of smart technologies in optimizing energy consumption and reducing operational costs is further contributing to the market expansion.
Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Government Polices
The Latvian government has been actively promoting the adoption and development of Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) through various policies and initiatives. These include providing financial incentives and subsidies to companies investing in IED technologies, fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders and research institutions to drive innovation, and implementing regulations to ensure the security and interoperability of IEDs. Additionally, the government has launched educational programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of professionals in the field of IEDs. Overall, the government`s policies aim to create a conducive environment for the growth of the Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market by supporting technological advancements, fostering innovation, and ensuring the safety and reliability of these devices.
Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market appears promising, driven by increasing investments in smart grid infrastructure and the growing adoption of IoT technology across various industries. The demand for intelligent electronic devices such as smart meters, sensors, and communication devices is expected to rise as Latvia continues to modernize its energy sector and improve efficiency in utilities management. Additionally, the government`s focus on promoting digitalization and sustainability initiatives is likely to further stimulate market growth. With advancements in technologies like AI and machine learning, the market is poised for innovation and expansion in areas such as smart homes, smart cities, and industrial automation, presenting opportunities for both local and international players to capitalize on this evolving landscape.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Outlook
- Market Size of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market, 2024
- Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market, 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Revenues & Volume for the Period 2021- 2031
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Trend Evolution
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Drivers and Challenges
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Price Trends
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Porter's Five Forces
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Industry Life Cycle
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Type for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Digital Relay for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Voltage Regulator for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Protection Relay for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Circuit Breaker Controller for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Load Tap Changer Controller for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Recloser Controller for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Capacitor Bank Switch for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Digital Relay Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Others for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Application for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Mass Transit System for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Traction Signaling & Control System for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Water Supply & Management System for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Automation for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume By Condition Monitoring for the Period 2021- 2031
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Import Export Trade Statistics
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Type
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Application
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Top Companies Market Share
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Competitive Benchmarking By Technical and Operational Parameters
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Company Profiles
- Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Key Strategic Recommendations
Frequently Asked Questions About the Market Study (FAQs):
1 Executive Summary |
2 Introduction |
2.1 Key Highlights of the Report |
2.2 Report Description |
2.3 Market Scope & Segmentation |
2.4 Research Methodology |
2.5 Assumptions |
3 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Overview |
3.1 Latvia Country Macro Economic Indicators |
3.2 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, 2021 & 2031F |
3.3 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market - Industry Life Cycle |
3.4 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market - Porter's Five Forces |
3.5 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Type, 2021 & 2031F |
3.6 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Application, 2021 & 2031F |
4 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Dynamics |
4.1 Impact Analysis |
4.2 Market Drivers |
4.2.1 Increasing demand for smart home solutions and automation in Latvia |
4.2.2 Government initiatives promoting the adoption of intelligent electronic devices |
4.2.3 Technological advancements leading to the development of innovative products |
4.3 Market Restraints |
4.3.1 High initial costs associated with intelligent electronic devices |
4.3.2 Limited consumer awareness and understanding of the benefits of such devices |
4.3.3 Concerns regarding data security and privacy issues with connected devices |
5 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Trends |
6 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market, By Types |
6.1 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market, By Type |
6.1.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.1.2 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Type, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.3 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Digital Relay, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.4 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Voltage Regulator, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.5 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Protection Relay, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.6 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Circuit Breaker Controller, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.7 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Load Tap Changer Controller, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.8 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Recloser Controller, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.9 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Others, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.10 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Others, 2021- 2031F |
6.2 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market, By Application |
6.2.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.2.2 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Mass Transit System, 2021- 2031F |
6.2.3 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Traction Signaling & Control System, 2021- 2031F |
6.2.4 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Water Supply & Management System, 2021- 2031F |
6.2.5 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Automation, 2021- 2031F |
6.2.6 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenues & Volume, By Condition Monitoring, 2021- 2031F |
7 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Import-Export Trade Statistics |
7.1 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Export to Major Countries |
7.2 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Imports from Major Countries |
8 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Key Performance Indicators |
8.1 Number of smart home installations in Latvia |
8.2 Percentage of households using intelligent electronic devices |
8.3 Growth in the number of IoT (Internet of Things) devices connected in Latvia |
9 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market - Opportunity Assessment |
9.1 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Opportunity Assessment, By Type, 2021 & 2031F |
9.2 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Opportunity Assessment, By Application, 2021 & 2031F |
10 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market - Competitive Landscape |
10.1 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Revenue Share, By Companies, 2024 |
10.2 Latvia Intelligent Electronic Devices Market Competitive Benchmarking, By Operating and Technical Parameters |
11 Company Profiles |
12 Recommendations |
13 Disclaimer |
Export potential assessment - trade Analytics for 2030
Export potential enables firms to identify high-growth global markets with greater confidence by combining advanced trade intelligence with a structured quantitative methodology. The framework analyzes emerging demand trends and country-level import patterns while integrating macroeconomic and trade datasets such as GDP and population forecasts, bilateral import–export flows, tariff structures, elasticity differentials between developed and developing economies, geographic distance, and import demand projections. Using weighted trade values from 2020–2024 as the base period to project country-to-country export potential for 2030, these inputs are operationalized through calculated drivers such as gravity model parameters, tariff impact factors, and projected GDP per-capita growth. Through an analysis of hidden potentials, demand hotspots, and market conditions that are most favorable to success, this method enables firms to focus on target countries, maximize returns, and global expansion with data, backed by accuracy.
By factoring in the projected importer demand gap that is currently unmet and could be potential opportunity, it identifies the potential for the Exporter (Country) among 190 countries, against the general trade analysis, which identifies the biggest importer or exporter.
To discover high-growth global markets and optimize your business strategy:
Click Here- Single User License$ 1,995
- Department License$ 2,400
- Site License$ 3,120
- Global License$ 3,795
Search
Thought Leadership and Analyst Meet
Our Clients
Related Reports
- India Switchgear Market Outlook (2026 - 2032) | Size, Share, Trends, Growth, Revenue, Forecast, Analysis, Value, Outlook
- Pakistan Contraceptive Implants Market (2025-2031) | Demand, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Companies, Challenges
- Sri Lanka Packaging Market (2026-2032) | Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges, Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints
- India Kids Watches Market (2026-2032) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Saudi Arabia Core Assurance Service Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Romania Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Market (2026-2032) | Industry, Analysis, Revenue, Size, Forecast, Outlook, Value, Trends, Share, Growth & Companies
- Saudi Arabia Car Window Tinting Film, Paint Protection Film (PPF), and Ceramic Coating Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- South Africa Stationery Market (2025-2031) | Share, Size, Industry, Value, Growth, Revenue, Analysis, Trends, Segmentation & Outlook
- Afghanistan Rocking Chairs And Adirondack Chairs Market (2026-2032) | Size & Revenue, Competitive Landscape, Share, Segmentation, Industry, Value, Outlook, Analysis, Trends, Growth, Forecast, Companies
- Afghanistan Apparel Market (2026-2032) | Growth, Outlook, Industry, Segmentation, Forecast, Size, Companies, Trends, Value, Share, Analysis & Revenue
Industry Events and Analyst Meet
Whitepaper
- Middle East & Africa Commercial Security Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East & Africa Fire Safety Systems & Equipment Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Drone Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East Lighting Fixture Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Physical & Perimeter Security Market Click here to view more.
6WResearch In News
- Doha a strategic location for EV manufacturing hub: IPA Qatar
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Empowering Growth: The Thriving Journey of Bangladesh’s Cable Industry
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Video call with a traditional healer? Once unthinkable, it’s now common in South Africa
- Intelligent Buildings To Smooth GCC’s Path To Net Zero


















