Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market (2025-2031) | Trends, Companies, Value, Forecast, Size & Revenue, Analysis, Share, Segmentation, Outlook, Growth, Competitive Landscape, Industry
| Product Code: ETC8053773 | Publication Date: Sep 2024 | Updated Date: Nov 2025 | Product Type: Market Research Report | |
| Publisher: 6Wresearch | Author: Sumit Sagar | No. of Pages: 75 | No. of Figures: 35 | No. of Tables: 20 |
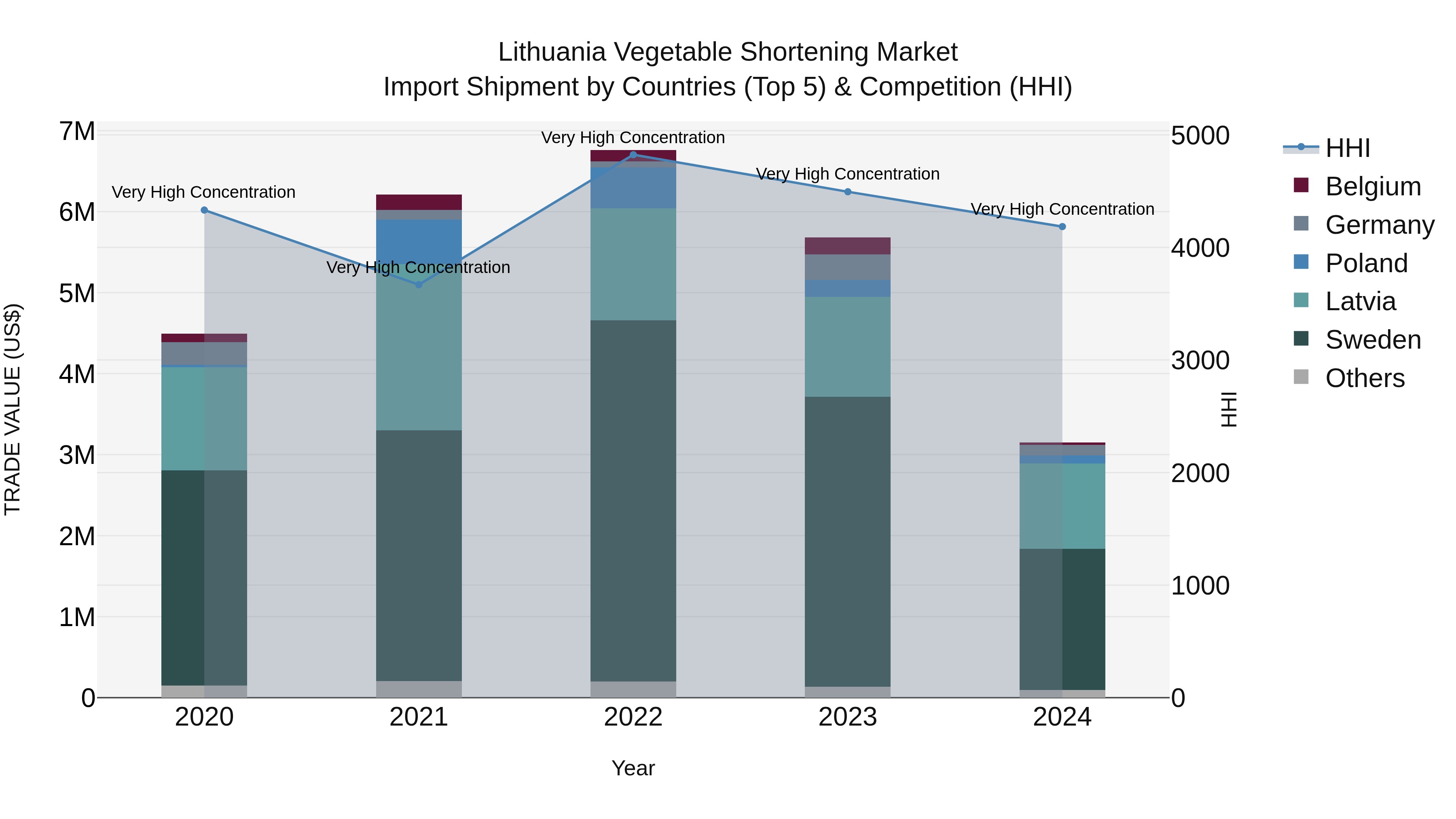
Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Top 5 Importing Countries and Market Competition (HHI) Analysis
The Lithuania vegetable shortening import market in 2024 continued to display a high level of concentration, with top exporting countries being Sweden, Latvia, Germany, Poland, and Netherlands. The market experienced a significant decline in both the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2020-24 at -8.49% and the growth rate from 2023-24 at -44.53%. This indicates a challenging environment for vegetable shortening imports in Lithuania, potentially influenced by various economic factors impacting trade dynamics.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Outlook
- Market Size of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market, 2024
- Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market, 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Revenues & Volume for the Period 2021- 2031
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Trend Evolution
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Drivers and Challenges
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Price Trends
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Porter's Five Forces
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Industry Life Cycle
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume By Form for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume By Dry for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume By Liquid for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume By Application for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume By Bakery and Confectionery for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume By Sweet and Savory Snacks for the Period 2021- 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume By Others for the Period 2021- 2031
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Import Export Trade Statistics
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Form
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Application
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Top Companies Market Share
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Competitive Benchmarking By Technical and Operational Parameters
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Company Profiles
- Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Key Strategic Recommendations
Frequently Asked Questions About the Market Study (FAQs):
1 Executive Summary |
2 Introduction |
2.1 Key Highlights of the Report |
2.2 Report Description |
2.3 Market Scope & Segmentation |
2.4 Research Methodology |
2.5 Assumptions |
3 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Overview |
3.1 Lithuania Country Macro Economic Indicators |
3.2 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume, 2021 & 2031F |
3.3 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market - Industry Life Cycle |
3.4 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market - Porter's Five Forces |
3.5 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Form, 2021 & 2031F |
3.6 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Application, 2021 & 2031F |
4 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Dynamics |
4.1 Impact Analysis |
4.2 Market Drivers |
4.2.1 Growing consumer awareness about health benefits of vegetable shortening as a substitute for other fats |
4.2.2 Increasing demand for convenience foods and baked goods in Lithuania |
4.2.3 Rise in disposable income leading to higher spending on premium food products |
4.3 Market Restraints |
4.3.1 Fluctuating prices of raw materials such as soybean oil, palm oil, and sunflower oil |
4.3.2 Health concerns related to consumption of processed foods containing vegetable shortening |
5 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Trends |
6 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market, By Types |
6.1 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market, By Form |
6.1.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.1.2 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume, By Form, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.3 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume, By Dry, 2021- 2031F |
6.1.4 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume, By Liquid, 2021- 2031F |
6.2 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market, By Application |
6.2.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.2.2 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume, By Bakery and Confectionery, 2021- 2031F |
6.2.3 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume, By Sweet and Savory Snacks, 2021- 2031F |
6.2.4 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenues & Volume, By Others, 2021- 2031F |
7 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Import-Export Trade Statistics |
7.1 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Export to Major Countries |
7.2 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Imports from Major Countries |
8 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Key Performance Indicators |
8.1 Consumer acceptance and perception of vegetable shortening as a healthier alternative |
8.2 Number of new product launches and innovations in the vegetable shortening market |
8.3 Adoption rate of vegetable shortening by food manufacturers for various applications |
9 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market - Opportunity Assessment |
9.1 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Opportunity Assessment, By Form, 2021 & 2031F |
9.2 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Opportunity Assessment, By Application, 2021 & 2031F |
10 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market - Competitive Landscape |
10.1 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Revenue Share, By Companies, 2024 |
10.2 Lithuania Vegetable Shortening Market Competitive Benchmarking, By Operating and Technical Parameters |
11 Company Profiles |
12 Recommendations |
13 Disclaimer |
Export potential assessment - trade Analytics for 2030
Export potential enables firms to identify high-growth global markets with greater confidence by combining advanced trade intelligence with a structured quantitative methodology. The framework analyzes emerging demand trends and country-level import patterns while integrating macroeconomic and trade datasets such as GDP and population forecasts, bilateral import–export flows, tariff structures, elasticity differentials between developed and developing economies, geographic distance, and import demand projections. Using weighted trade values from 2020–2024 as the base period to project country-to-country export potential for 2030, these inputs are operationalized through calculated drivers such as gravity model parameters, tariff impact factors, and projected GDP per-capita growth. Through an analysis of hidden potentials, demand hotspots, and market conditions that are most favorable to success, this method enables firms to focus on target countries, maximize returns, and global expansion with data, backed by accuracy.
By factoring in the projected importer demand gap that is currently unmet and could be potential opportunity, it identifies the potential for the Exporter (Country) among 190 countries, against the general trade analysis, which identifies the biggest importer or exporter.
To discover high-growth global markets and optimize your business strategy:
Click Here- Single User License$ 1,995
- Department License$ 2,400
- Site License$ 3,120
- Global License$ 3,795
Search
Thought Leadership and Analyst Meet
Our Clients
Related Reports
- India Switchgear Market Outlook (2026 - 2032) | Size, Share, Trends, Growth, Revenue, Forecast, Analysis, Value, Outlook
- Pakistan Contraceptive Implants Market (2025-2031) | Demand, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Companies, Challenges
- Sri Lanka Packaging Market (2026-2032) | Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges, Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints
- India Kids Watches Market (2026-2032) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Saudi Arabia Core Assurance Service Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Romania Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Market (2026-2032) | Industry, Analysis, Revenue, Size, Forecast, Outlook, Value, Trends, Share, Growth & Companies
- Saudi Arabia Car Window Tinting Film, Paint Protection Film (PPF), and Ceramic Coating Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- South Africa Stationery Market (2025-2031) | Share, Size, Industry, Value, Growth, Revenue, Analysis, Trends, Segmentation & Outlook
- Afghanistan Rocking Chairs And Adirondack Chairs Market (2026-2032) | Size & Revenue, Competitive Landscape, Share, Segmentation, Industry, Value, Outlook, Analysis, Trends, Growth, Forecast, Companies
- Afghanistan Apparel Market (2026-2032) | Growth, Outlook, Industry, Segmentation, Forecast, Size, Companies, Trends, Value, Share, Analysis & Revenue
Industry Events and Analyst Meet
Whitepaper
- Middle East & Africa Commercial Security Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East & Africa Fire Safety Systems & Equipment Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Drone Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East Lighting Fixture Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Physical & Perimeter Security Market Click here to view more.
6WResearch In News
- Doha a strategic location for EV manufacturing hub: IPA Qatar
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Empowering Growth: The Thriving Journey of Bangladesh’s Cable Industry
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Video call with a traditional healer? Once unthinkable, it’s now common in South Africa
- Intelligent Buildings To Smooth GCC’s Path To Net Zero


















