Japan Affordable Housing Market (2025-2031) | Segmentation, Opportunities, Companies, Value, Drivers, Outlook, Segments, Growth, Forecast, Consumer Insights, Challenges, Trends, Strategy, Competition, Investment Trends, Strategic Insights, Size, Analysis, Supply, Demand, Restraints, Share, Industry, Competitive, Pricing Analysis, Revenue
| Product Code: ETC12661522 | Publication Date: Apr 2025 | Updated Date: Oct 2025 | Product Type: Market Research Report | |
| Publisher: 6Wresearch | Author: Dhaval Chaurasia | No. of Pages: 65 | No. of Figures: 34 | No. of Tables: 19 |
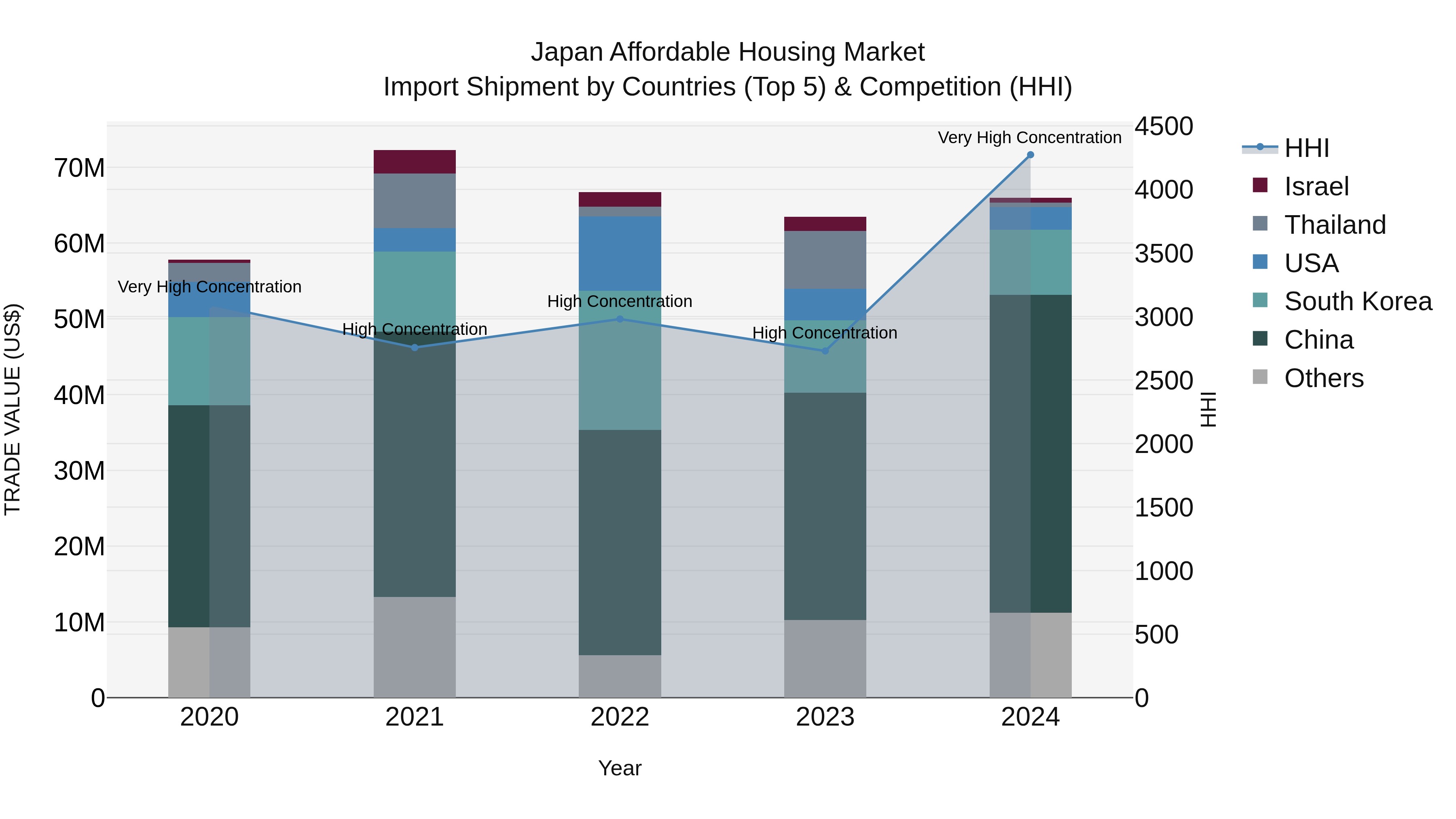
Japan Affordable Housing Market Import Shipment by Countries (Top 5) & Competition (HHI)
The Japan affordable housing import market continues to witness steady growth, with key exporting countries including China, South Korea, USA, Netherlands, and Indonesia dominating the market in 2024. The market concentration, as measured by the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI), has significantly increased from 2023 to 2024, indicating a more competitive landscape. With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.37% from 2020 to 2024 and a growth rate of 4.0% from 2023 to 2024, the market shows promising opportunities for both importers and exporters in the affordable housing sector.
Japan Affordable Housing Market Overview
The Japan affordable housing market is a growing sector driven by the country`s aging population and increasing urbanization. With a focus on providing housing solutions for low to middle-income individuals, developers are increasingly investing in affordable housing projects in major cities like Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya. The government plays a significant role in promoting affordable housing through subsidies, tax incentives, and regulatory support. Additionally, initiatives such as the Rental Housing Market Stabilization Act aim to ensure fair and affordable rental prices for tenants. Despite these efforts, challenges remain in meeting the high demand for affordable housing, particularly in densely populated urban areas. Overall, the Japan affordable housing market presents opportunities for developers, investors, and policymakers to address the housing needs of a diverse and growing population.
Japan Affordable Housing Market Trends
In Japan, the affordable housing market is experiencing a trend towards smaller, more efficient living spaces to cater to the needs of a growing population of single-person households, young professionals, and seniors. This trend is driven by factors such as rising land prices in urban areas, changing lifestyle preferences, and a focus on sustainability. Developers are increasingly incorporating smart design solutions, such as modular construction and shared amenities, to maximize space utilization and keep costs down. The demand for affordable housing options is also prompting the government to implement policies and incentives to encourage the development of more affordable housing units. Overall, the market is seeing a shift towards innovative and cost-effective housing solutions to meet the diverse needs of Japanese residents.
Japan Affordable Housing Market Challenges
In the Japan affordable housing market, one of the main challenges is the limited availability of land for development, particularly in urban areas. This scarcity of land drives up property prices, making it difficult for developers to offer affordable housing options. Additionally, stringent regulations and zoning restrictions further complicate the development process, leading to higher construction costs and longer timelines for project completion. Another challenge is the high demand for rental housing in major cities like Tokyo and Osaka, which puts pressure on the limited supply of affordable rental units. To address these issues, policymakers, developers, and urban planners need to collaborate on innovative solutions such as incentivizing redevelopment of underutilized spaces, promoting mixed-use developments, and streamlining the regulatory processes to make affordable housing more accessible to the growing population in Japan.
Japan Affordable Housing Market Investment Opportunities
Investment opportunities in the Japan affordable housing market are currently promising due to the increasing demand for affordable housing options, particularly in urban areas. With a growing population and low interest rates, investors can explore opportunities in developing or acquiring affordable housing properties. Additionally, the Japanese government has been implementing policies to incentivize the construction of affordable housing, providing potential tax benefits and subsidies for developers. Investing in affordable housing projects or real estate investment trusts (REITs) focused on this market segment could offer attractive returns and a socially responsible investment option. However, investors should conduct thorough market research and due diligence to understand the local regulations, demographics, and market dynamics before making investment decisions in the Japan affordable housing sector.
Japan Affordable Housing Market Government Policy
The Japanese government has implemented various policies to address the issue of affordable housing in the country. One key initiative is the Promotion of Urban Renaissance project, which aims to revitalize urban areas and promote the development of affordable housing. Additionally, the government provides subsidies and tax incentives to encourage the construction of affordable housing units. The Housing and Urban Development Corporation (HUDC) also plays a significant role in providing financial support and technical assistance for affordable housing projects. Furthermore, there are regulations in place to ensure the availability of affordable housing for low-income households, such as the Public Housing Act and the Urban Renaissance Agency Act. Overall, the Japanese government is actively working to improve access to affordable housing for its citizens through a combination of policy measures and support programs.
Japan Affordable Housing Market Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Japan affordable housing market appears promising due to several factors. With an aging population and a declining birth rate, there is a growing demand for smaller, more affordable housing units. Additionally, the government has been implementing policies to promote affordable housing development, such as tax incentives and subsidies for construction. The increasing popularity of compact living spaces and shared housing concepts among younger generations also contribute to the growth of the affordable housing market. As urban areas become more densely populated, the need for affordable housing options will continue to rise. Overall, the Japan affordable housing market is expected to expand in the coming years, presenting opportunities for developers and investors to cater to this evolving demand.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Japan Affordable Housing Market Outlook
- Market Size of Japan Affordable Housing Market, 2024
- Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market, 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Revenues & Volume for the Period 2021-2031
- Japan Affordable Housing Market Trend Evolution
- Japan Affordable Housing Market Drivers and Challenges
- Japan Affordable Housing Price Trends
- Japan Affordable Housing Porter's Five Forces
- Japan Affordable Housing Industry Life Cycle
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Product Type for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Multi-Family Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Single-Family Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Modular Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Financing Type for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Government-Sponsored Programs for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Subsidized Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Private Financing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By End User for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By First-time Homebuyers for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Low-Income Families for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Senior Citizens for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Veterans for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Builder Type for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Public Sector for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Private Sector for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Mixed-Use Developments for the Period 2021-2031
- Japan Affordable Housing Import Export Trade Statistics
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Product Type
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Financing Type
- Market Opportunity Assessment By End User
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Builder Type
- Japan Affordable Housing Top Companies Market Share
- Japan Affordable Housing Competitive Benchmarking By Technical and Operational Parameters
- Japan Affordable Housing Company Profiles
- Japan Affordable Housing Key Strategic Recommendations
Frequently Asked Questions About the Market Study (FAQs):
1 Executive Summary |
2 Introduction |
2.1 Key Highlights of the Report |
2.2 Report Description |
2.3 Market Scope & Segmentation |
2.4 Research Methodology |
2.5 Assumptions |
3 Japan Affordable Housing Market Overview |
3.1 Japan Country Macro Economic Indicators |
3.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, 2021 & 2031F |
3.3 Japan Affordable Housing Market - Industry Life Cycle |
3.4 Japan Affordable Housing Market - Porter's Five Forces |
3.5 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Product Type, 2021 & 2031F |
3.6 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Financing Type, 2021 & 2031F |
3.7 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By End User, 2021 & 2031F |
3.8 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Builder Type, 2021 & 2031F |
4 Japan Affordable Housing Market Dynamics |
4.1 Impact Analysis |
4.2 Market Drivers |
4.2.1 Government initiatives and policies to promote affordable housing |
4.2.2 Increasing urbanization leading to a higher demand for affordable housing |
4.2.3 Growing population and changing demographics increasing the need for affordable housing |
4.3 Market Restraints |
4.3.1 High land and construction costs impacting the affordability of housing |
4.3.2 Economic conditions affecting the purchasing power of potential buyers |
4.3.3 Limited availability of suitable land for affordable housing development |
5 Japan Affordable Housing Market Trends |
6 Japan Affordable Housing Market, By Types |
6.1 Japan Affordable Housing Market, By Product Type |
6.1.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.1.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Product Type, 2021 - 2031F |
6.1.3 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Multi-Family Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.1.4 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Single-Family Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.1.5 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Modular Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market, By Financing Type |
6.2.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.2.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Government-Sponsored Programs, 2021 - 2031F |
6.2.3 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Subsidized Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.2.4 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Private Financing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3 Japan Affordable Housing Market, By End User |
6.3.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.3.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By First-time Homebuyers, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3.3 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Low-Income Families, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3.4 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Senior Citizens, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3.5 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Veterans, 2021 - 2031F |
6.4 Japan Affordable Housing Market, By Builder Type |
6.4.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.4.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Public Sector, 2021 - 2031F |
6.4.3 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Private Sector, 2021 - 2031F |
6.4.4 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Mixed-Use Developments, 2021 - 2031F |
7 Japan Affordable Housing Market Import-Export Trade Statistics |
7.1 Japan Affordable Housing Market Export to Major Countries |
7.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Imports from Major Countries |
8 Japan Affordable Housing Market Key Performance Indicators |
8.1 Percentage of government budget allocated to affordable housing initiatives |
8.2 Housing affordability index reflecting the ratio of median household income to median house price |
8.3 Number of new affordable housing units constructed annually |
8.4 Average time taken for approval of affordable housing projects |
8.5 Percentage of population living in affordable housing compared to total population |
9 Japan Affordable Housing Market - Opportunity Assessment |
9.1 Japan Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By Product Type, 2021 & 2031F |
9.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By Financing Type, 2021 & 2031F |
9.3 Japan Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By End User, 2021 & 2031F |
9.4 Japan Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By Builder Type, 2021 & 2031F |
10 Japan Affordable Housing Market - Competitive Landscape |
10.1 Japan Affordable Housing Market Revenue Share, By Companies, 2024 |
10.2 Japan Affordable Housing Market Competitive Benchmarking, By Operating and Technical Parameters |
11 Company Profiles |
12 Recommendations |
13 Disclaimer |
- Single User License$ 1,995
- Department License$ 2,400
- Site License$ 3,120
- Global License$ 3,795
Search
Thought Leadership and Analyst Meet
Our Clients
Related Reports
- Germany Breakfast Food Market (2026-2032) | Industry, Share, Growth, Size, Companies, Value, Analysis, Revenue, Trends, Forecast & Outlook
- Australia Briquette Market (2025-2031) | Growth, Size, Revenue, Forecast, Analysis, Trends, Value, Share, Industry & Companies
- Vietnam System Integrator Market (2025-2031) | Size, Companies, Analysis, Industry, Value, Forecast, Growth, Trends, Revenue & Share
- ASEAN and Thailand Brain Health Supplements Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- ASEAN Bearings Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Europe Flooring Market (2025-2031) | Outlook, Share, Industry, Trends, Forecast, Companies, Revenue, Size, Analysis, Growth & Value
- Saudi Arabia Manlift Market (2025-2031) | Outlook, Size, Growth, Trends, Companies, Industry, Revenue, Value, Share, Forecast & Analysis
- Uganda Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Rwanda Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Kenya Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
Industry Events and Analyst Meet
Whitepaper
- Middle East & Africa Commercial Security Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East & Africa Fire Safety Systems & Equipment Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Drone Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East Lighting Fixture Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Physical & Perimeter Security Market Click here to view more.
6WResearch In News
- Doha a strategic location for EV manufacturing hub: IPA Qatar
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Empowering Growth: The Thriving Journey of Bangladesh’s Cable Industry
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Video call with a traditional healer? Once unthinkable, it’s now common in South Africa
- Intelligent Buildings To Smooth GCC’s Path To Net Zero


















