US Inverter Market (2025-2031) | Outlook, Value, Industry, Size, Share, Trends, Companies, Revenue, Analysis, Growth, Forecast
Market Forecast By Type (Solar Inverters, Vehicle Inverter, others), By Output Power Rating (Upto 10 kW, 10-50 kW, 51-100 kW, above 100 kW), By End User (PV Plants, Residential, Automotive) And Competitive Landscape
| Product Code: ETC4530722 | Publication Date: Jul 2023 | Updated Date: Nov 2025 | Product Type: Report | |
| Publisher: 6Wresearch | Author: Ravi Bhandari | No. of Pages: 70 | No. of Figures: 35 | No. of Tables: 3 |
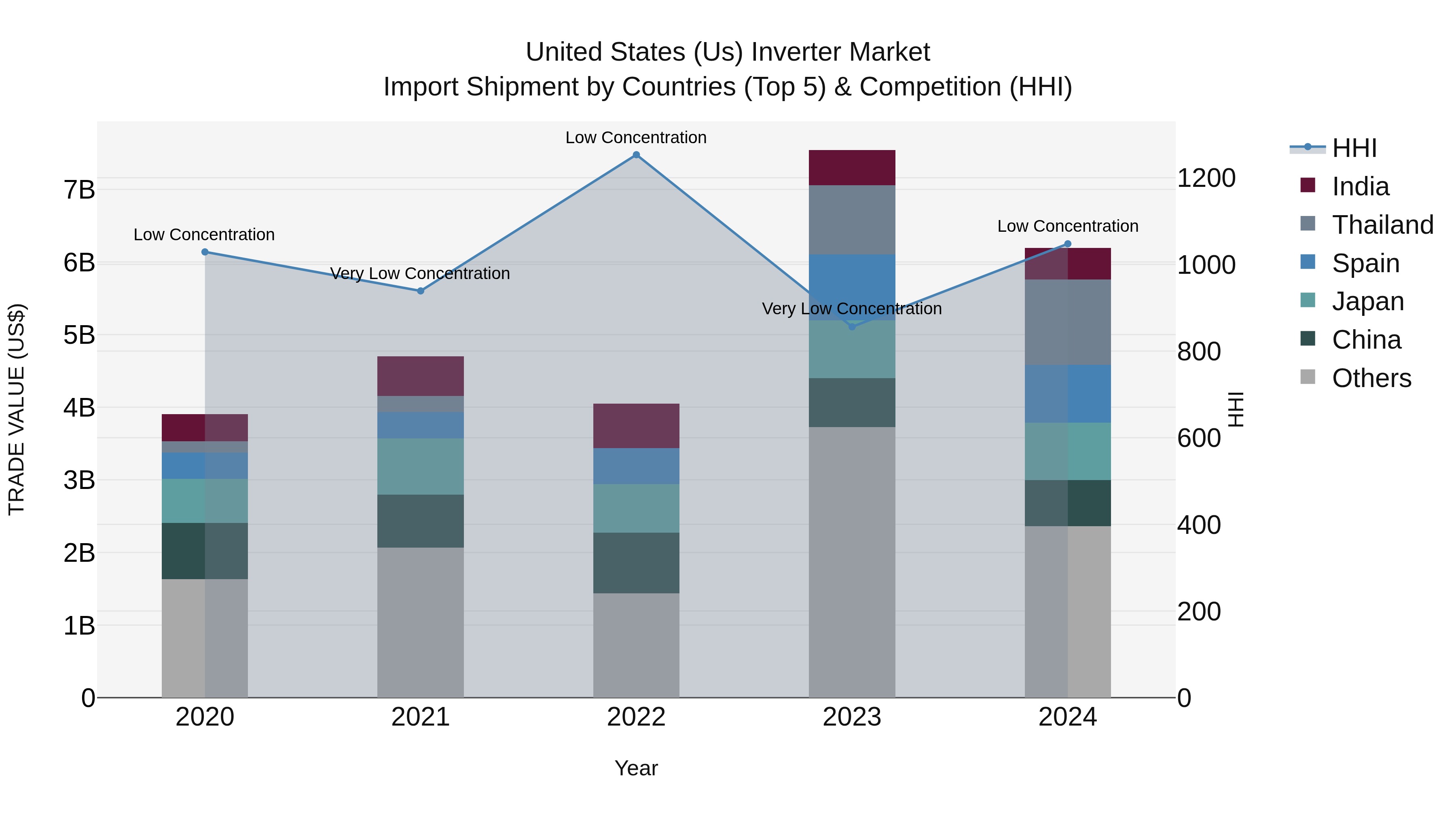
United States (US) Inverter Market Top 5 Importing Countries and Market Competition (HHI) Analysis
In 2024, the United States saw a diverse range of inverter imports coming primarily from Thailand, Spain, Japan, China, and Mexico. The market showed a shift from very low concentration in 2023 to low concentration in 2024, indicating a more balanced distribution among exporting countries. Despite a slight decline in growth rate from 2023 to 2024, the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for 2020-2024 remained strong at 12.24%. This data suggests a resilient and evolving market landscape for inverter imports in the United States, with opportunities for continued growth and diversification in the coming years.
US Inverter Market Highlights
| Report Name | US Inverter Market |
| Forecast period | 2025-2031 |
| CAGR | 11.8% |
| Growing Sector | PV Plants |
Topics Covered in the US Inverter Market Report
The US Inverter market report thoroughly covers the market by type, by output power rating, by end user and competitive Landscape. The report provides an unbiased and detailed analysis of the on-going market trends, opportunities/high growth areas, and market drivers which would help the stakeholders to devise and align their market strategies according to the current and future market dynamics.
United States Inverter Market Synopsis
The U.S. inverter market is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, government policies, and increasing investor interest in renewable projects. Additionally, The US inverter market is witnessing several trends, which are shaping its future. First, there has been a shift from large centralized solar power plants to smaller distributed-scale residential and commercial solar projects. Second, there has been an increase in the adoption of battery storage systems, which are coupled with solar inverters to provide grid stability and back-up power. Third, micro-inverters and power optimizers are becoming more popular, as they increase the efficiency and flexibility of solar PV systems. However, despite the growth prospects, the United States inverter industry faces several challenges that need to be addressed. First, there is stiff competition among companies, which has resulted in pricing pressures on manufacturers. Second, the lack of standardization in the inverters’ design and performance specifications has led to interoperability issues between different PV modules and inverters. Third, the U.S. inverter market faces significant import tariffs on Chinese-made inverters, which limits the competitive pricing options.
According to 6Wresearch, US Inverter market size is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.8% during 2025-2031. The increase in renewable energy uptake, favorable government policies, urbanization, technological innovation, and energy efficiency awareness is driving market growth. The United States inverter market is experiencing an increase in demand due to the growing adoption of renewable energy technologies. The electric power industry is transitioning from fossil fuels to cleaner and sustainable energy sources. Some of the renewable energy sources that are driving market growth include solar, wind, and hydroelectric. Inverters help facilitate the conversion of DC current into AC current, which is essential for renewable energy systems. As more individuals and businesses invest in renewable energy, the demand for inverters is expected to surge. Further, urbanization is a significant driver of the inverter market in the United States. As more people move to cities, the demand for energy increases. The construction of new buildings and increased urbanization has resulted in a surge in demand for inverters. Residential buildings require efficient power conversion systems, and inverters can help meet the demand. The increasing trend of residential electrification has also contributed significantly to the growth of the inverter market in the United States.
Government Initiatives Introduced in the US Inverter Market
The first significant government initiative that drives the United States inverter market is the Investment Tax Credit (ITC). The tax credit has been a cornerstone support program in the renewable energy sector, bringing financial benefits to individuals and businesses that invest in renewable energy systems. The current ITC credit is 26% of the total cost of a renewable energy system, including inverters, and it will remain applicable until 2022. This ITC credit significantly reduces the payback period for the initial investment, thereby encouraging adoption of renewable energy, including using inverters. These programs have boosted the US Inverter Market Share. Further, the Clean Energy Standard (CES), another government initiative, is focused on promoting energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions across all sectors of the economy. To achieve this aim, the CES relies on the use of inverters as a vital component of renewable energy systems. The CES requires utilities to generate a specific percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, with penalties for non-compliance. This requirement drives the adoption of renewable energy systems, including inverters.
Key Players in the US Inverter Market
The United States inverter market is dominated by a handful of players, including SMA Solar Technology, ABB, Solaredge Technologies, Enphase Energy, and Fronius International. These companies offer a range of products from string inverters for residential and commercial rooftop installations to central inverters for utility-scale solar and wind projects. Additionally, these companies also grip huge US Inverter Market Revenues. Also, SMA Solar Technology is one of the largest players in the market, offering high-quality and reliable inverters for all types of solar installations. ABB is another major player, known for its latest PVS-175 string solar inverter, one of the most efficient products in the industry.
Future Insights of the US Inverter Market
The United States inverter market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, with the increasing demand for renewable energy, energy storage, and government support and policies. With technological advancements, inverter manufacturers will develop better and more efficient inverters to meet the evolving needs of the market. The competitive landscape of the market will also drive down the cost of inverters, making them more accessible to consumers. The future of the United States inverter market looks promising, and manufacturers need to keep up with the ever-changing market trends to remain competitive.
Market Analysis by Type
According to Ravi Bhandari, Research Head, 6Wresearch, solar inverters are critical components in solar PV systems, and they are designed to handle DC power produced by solar panels and convert it into usable AC power. Nowadays, inverters come in many types, including string inverters, central inverters, micro-inverters, and power optimizers. String inverters are the most commonly used type of inverter because they are affordable and easy to install. On the other hand, micro-inverters are installed on each solar panel and provide a greater degree of flexibility. Power optimizers, meanwhile, are usually paired with string inverters and optimize power production by increasing energy harvest efficiency by thirty percent. Further, a vehicle inverter is a device that converts DC power from a car's battery into AC power. It is crucial for modern electric vehicles that rely on inverters to power their motors, radios, lights, and other functions.
Market Analysis by End users
The first significant end-user of inverters is PV Plants. These are large-scale power generation systems that consist of numerous photovoltaic modules and panels. The United States is a top producer of solar electricity, with over 97GW of solar capacity installed across the country. The majority of these solar plants use inverters to convert the DC current produced by the modules into useable AC power. In recent years, there has been a significant shift in the market, with the adoption of utility-scale inverters using advanced technologies like string and central inverters. This shift has led to improved efficiencies, reduced costs and minimal system maintenance, which is highly preferred by commercial energy providers. Moreover, the second end-user of inverters is residential. Residential solar power systems are designed for individual homes, and they comprise a few photovoltaic panels and modules. These solar systems operate regularly to provide energy for use within the home or to feed the grid. The inverters installed here aren't as powerful as those used in photovoltaic plants. They are typically smaller and operate at a lower voltage, which is perfect for home use. One of the significant benefits of using residential solar power systems is that it enables homeowners to generate their power and reduce their reliance on traditional grid power.
Key Attractiveness of the Report
- 10 Years Market Numbers.
- Historical Data Starting from 2021 to 2024.
- Base Year: 2024.
- Forecast Data until 2031.
- Key Performance Indicators Impacting the Market.
- Major Upcoming Developments and Projects.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- US Inverter Market Overview
- US Inverter Market Outlook
- US Inverter Market Forecast
- Market Size of US Inverter Market, 2024
- Forecast of US Inverter Market, 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Revenues & Volume for the Period 2021 - 2031
- US Inverter Market Trend Evolution
- US Inverter Market Drivers and Challenges
- US Inverter Price Trends
- US Inverter Porter's Five Forces
- US Inverter Industry Life Cycle
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By Type for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By Solar Inverters for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By Vehicle Inverter for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By others for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By Output Power Rating for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By Upto 10 kW for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By 10-50 kW for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By 51-100 kW for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By above 100 kW for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By End User for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By PV Plants for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By Residential for the Period 2021 - 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume By Automotive for the Period 2021 - 2031
- US Inverter Import Export Trade Statistics
- Market Opportunity Assessment, By Type
- Market Opportunity Assessment, By Output Power Rating
- Market Opportunity Assessment, By End User
- US Inverter Top Companies Market Share
- US Inverter Competitive Benchmarking, By Technical and Operational Parameters
- US Inverter Company Profiles
- US Inverter Key Strategic Recommendations
Markets Covered
The US Inverter market report provides a detailed analysis of the following market segments:
By Type
- Solar Inverters
- Vehicle Inverter
- Others
By Output Power Rating
- Upto 10 KW
- 10-50 KW
- 51-100 KW
- Above 100 KW
By End User
- PV Plants
- Residential
- Automotive
US Inverter Market (2025-2031): FAQs
| 1 Executive Summary |
| 2 Introduction |
| 2.1 Key Highlights of the Report |
| 2.2 Report Description |
| 2.3 Market Scope & Segmentation |
| 2.4 Research Methodology |
| 2.5 Assumptions |
| 3 US Inverter Market Overview |
| 3.1 US Country Macro Economic Indicators |
| 3.2 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, 2021 & 2031F |
| 3.3 US Inverter Market - Industry Life Cycle |
| 3.4 US Inverter Market - Porter's Five Forces |
| 3.5 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Type, 2021 & 2031F |
| 3.6 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Output Power Rating, 2021 & 2031F |
| 3.7 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume Share, By End User, 2021 & 2031F |
| 4 US Inverter Market Dynamics |
| 4.1 Impact Analysis |
| 4.2 Market Drivers |
| 4.2.1 Increasing adoption of renewable energy sources in the US, leading to the higher demand for inverters. |
| 4.2.2 Government initiatives and policies promoting clean energy solutions. |
| 4.2.3 Growing investment in utility-scale solar projects driving the inverter market. |
| 4.3 Market Restraints |
| 4.3.1 Intense competition among inverter manufacturers leading to pricing pressures. |
| 4.3.2 Regulatory uncertainties impacting market growth. |
| 4.3.3 Supply chain disruptions affecting the production and distribution of inverters. |
| 5 US Inverter Market Trends |
| 6 US Inverter Market, By Types |
| 6.1 US Inverter Market, By Type |
| 6.1.1 Overview and Analysis |
| 6.1.2 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By Type, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.1.3 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By Solar Inverters, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.1.4 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By Vehicle Inverter, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.1.5 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By others, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.2 US Inverter Market, By Output Power Rating |
| 6.2.1 Overview and Analysis |
| 6.2.2 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By Upto 10 kW, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.2.3 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By 10-50 kW, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.2.4 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By 51-100 kW, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.2.5 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By above 100 kW, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.3 US Inverter Market, By End User |
| 6.3.1 Overview and Analysis |
| 6.3.2 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By PV Plants, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.3.3 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By Residential, 2021 - 2031F |
| 6.3.4 US Inverter Market Revenues & Volume, By Automotive, 2021 - 2031F |
| 7 US Inverter Market Import-Export Trade Statistics |
| 7.1 US Inverter Market Export to Major Countries |
| 7.2 US Inverter Market Imports from Major Countries |
| 8 US Inverter Market Key Performance Indicators |
| 8.1 Average selling price (ASP) of inverters. |
| 8.2 Adoption rate of solar and wind energy in the US. |
| 8.3 Number of utility-scale solar projects in the pipeline. |
| 8.4 Efficiency improvements in inverter technology. |
| 8.5 Level of investment in research and development for next-gen inverters. |
| 9 US Inverter Market - Opportunity Assessment |
| 9.1 US Inverter Market Opportunity Assessment, By Type, 2021 & 2031F |
| 9.2 US Inverter Market Opportunity Assessment, By Output Power Rating, 2021 & 2031F |
| 9.3 US Inverter Market Opportunity Assessment, By End User, 2021 & 2031F |
| 10 US Inverter Market - Competitive Landscape |
| 10.1 US Inverter Market Revenue Share, By Companies, 2024 |
| 10.2 US Inverter Market Competitive Benchmarking, By Operating and Technical Parameters |
| 11 Company Profiles |
| 12 Recommendations |
| 13 Disclaimer |
- Single User License$ 1,995
- Department License$ 2,400
- Site License$ 3,120
- Global License$ 3,795
Search
Thought Leadership and Analyst Meet
Our Clients
Related Reports
- Germany Breakfast Food Market (2026-2032) | Industry, Share, Growth, Size, Companies, Value, Analysis, Revenue, Trends, Forecast & Outlook
- Australia Briquette Market (2025-2031) | Growth, Size, Revenue, Forecast, Analysis, Trends, Value, Share, Industry & Companies
- Vietnam System Integrator Market (2025-2031) | Size, Companies, Analysis, Industry, Value, Forecast, Growth, Trends, Revenue & Share
- ASEAN and Thailand Brain Health Supplements Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- ASEAN Bearings Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Europe Flooring Market (2025-2031) | Outlook, Share, Industry, Trends, Forecast, Companies, Revenue, Size, Analysis, Growth & Value
- Saudi Arabia Manlift Market (2025-2031) | Outlook, Size, Growth, Trends, Companies, Industry, Revenue, Value, Share, Forecast & Analysis
- Uganda Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Rwanda Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Kenya Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
Industry Events and Analyst Meet
Whitepaper
- Middle East & Africa Commercial Security Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East & Africa Fire Safety Systems & Equipment Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Drone Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East Lighting Fixture Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Physical & Perimeter Security Market Click here to view more.
6WResearch In News
- Doha a strategic location for EV manufacturing hub: IPA Qatar
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Empowering Growth: The Thriving Journey of Bangladesh’s Cable Industry
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Video call with a traditional healer? Once unthinkable, it’s now common in South Africa
- Intelligent Buildings To Smooth GCC’s Path To Net Zero


















