Netherlands Affordable Housing Market (2025-2031) | Supply, Size, Share, Consumer Insights, Segmentation, Competitive, Drivers, Forecast, Opportunities, Segments, Demand, Investment Trends, Analysis, Competition, Outlook, Strategy, Companies, Growth, Revenue, Industry, Challenges, Pricing Analysis, Strategic Insights, Trends, Restraints, Value
| Product Code: ETC12661644 | Publication Date: Apr 2025 | Updated Date: Nov 2025 | Product Type: Market Research Report | |
| Publisher: 6Wresearch | Author: Sumit Sagar | No. of Pages: 65 | No. of Figures: 34 | No. of Tables: 19 |
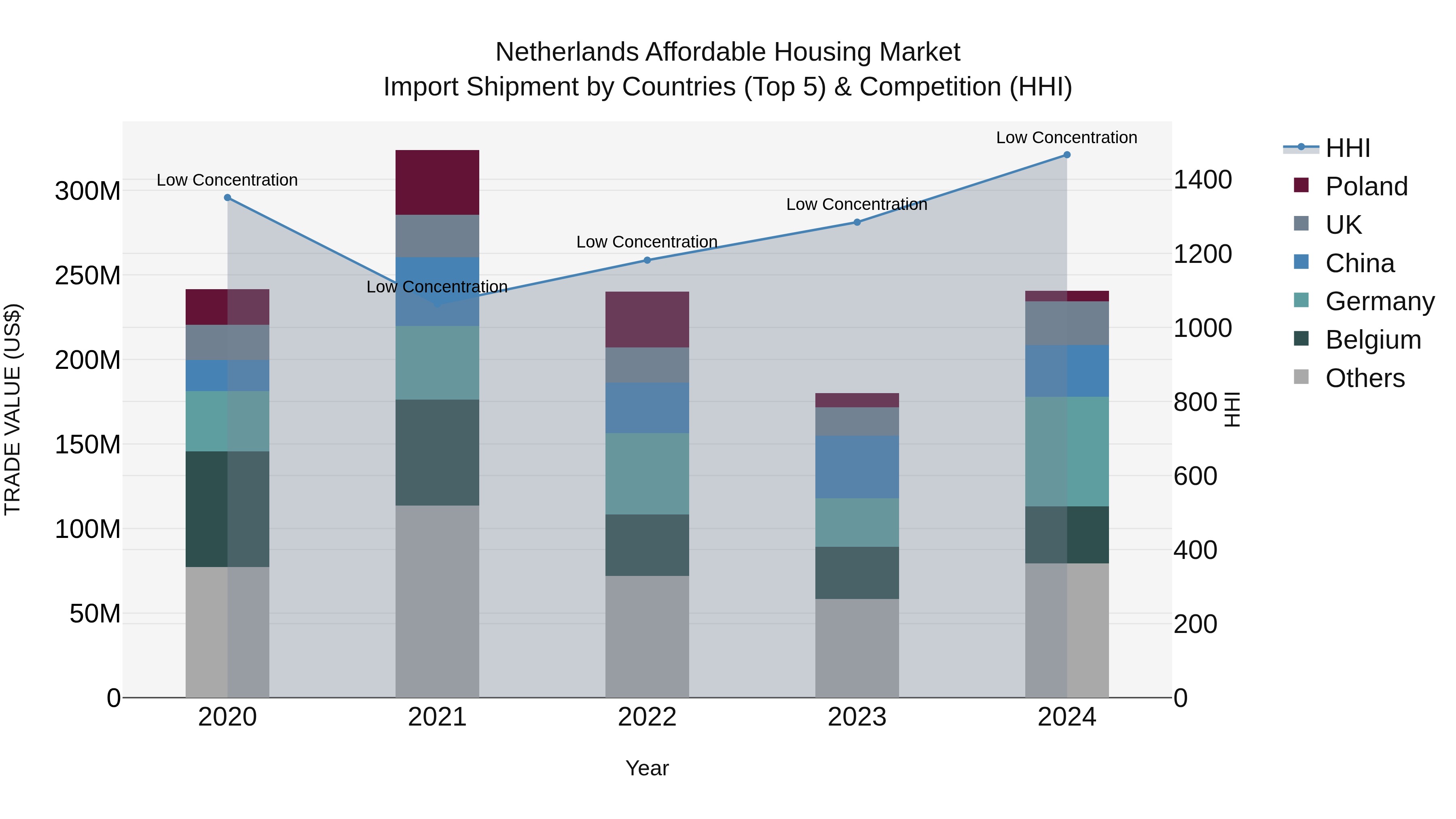
Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Top 5 Importing Countries and Market Competition (HHI) Analysis
Netherlands continues to see a diverse range of countries exporting affordable housing products, with top contributors being Germany, Metropolitan France, Belgium, China, and the UK in 2024. The market shows low concentration with a stable Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) in the same year. Despite a slight decline in the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) from 2020 to 2024, there was a notable growth rate of 33.73% from 2023 to 2024. This indicates a dynamic market landscape and potential opportunities for further development and expansion in the affordable housing sector in the Netherlands.
Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Overview
The Netherlands affordable housing market is characterized by a shortage of available properties, leading to high demand and rising prices. Affordable housing initiatives and social housing programs play a crucial role in providing accessible accommodation for low to moderate-income individuals. The government sets income limits for eligibility in these programs, with rent controlled to ensure affordability. However, the increasing population in urban areas like Amsterdam and Utrecht has put pressure on the market, resulting in challenges for those seeking affordable housing. Investors are also active in the market, further driving up prices. Overall, the Netherlands affordable housing market faces ongoing issues of supply and demand imbalance, necessitating continued efforts to address affordability and accessibility for all residents.
Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Trends
In the Netherlands, the affordable housing market is currently facing challenges due to a shortage of available properties, particularly in urban areas. This scarcity has led to increasing demand and rising prices, making it harder for lower-income individuals and families to find suitable housing options. As a result, there is a growing focus on initiatives to promote the development of more affordable housing units, such as government subsidies, incentives for affordable housing construction, and partnerships between public and private sectors. Additionally, there is a trend towards the repurposing of existing buildings for affordable housing projects and the implementation of sustainable and energy-efficient solutions to reduce costs for tenants. Overall, the Netherlands affordable housing market is seeking innovative strategies to address the affordability issue and create more inclusive housing options for all income levels.
Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Challenges
In the Netherlands, the affordable housing market faces challenges such as a shortage of available housing units, especially in popular urban areas like Amsterdam and Utrecht. This scarcity drives up prices, making it difficult for low to moderate-income individuals and families to find affordable housing options. Additionally, there is a lack of new affordable housing developments being built, further exacerbating the problem. The increasing demand for housing, coupled with strict regulations on construction and zoning laws, hinders the ability to quickly address the affordability issue. These challenges create a situation where many residents struggle to find suitable and affordable housing, leading to overcrowding, long waiting lists for social housing, and rising homelessness rates. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach involving government intervention, private sector investment, and community initiatives to increase the supply of affordable housing options.
Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Investment Opportunities
In the Netherlands, the affordable housing market presents several promising investment opportunities. With increasing urbanization and a growing population, there is a high demand for affordable housing units. Investors can consider opportunities in the development and renovation of affordable housing projects, as well as the acquisition of existing properties for rental purposes. Government initiatives and incentives aimed at promoting affordable housing also create a favorable investment environment. Additionally, the stable economy and strong rental market in the Netherlands provide investors with potential for long-term returns. Collaborating with local housing associations or developers can be beneficial for navigating the regulatory landscape and identifying attractive investment prospects in the affordable housing sector.
Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Government Policy
The Netherlands government has implemented several policies to address the challenges in the affordable housing market. These include regulations on rent levels, subsidies for social housing, and initiatives to increase the supply of affordable homes. The government sets maximum allowable rent increases, especially for properties in the social housing sector, to prevent excessive cost burdens on tenants. Subsidies are provided to housing associations to maintain and develop affordable housing units. Additionally, efforts are being made to streamline planning regulations and increase the construction of new affordable homes to meet the growing demand. Overall, the government`s focus is on ensuring a fair and sustainable housing market that provides affordable options for all residents.
Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Netherlands affordable housing market is expected to remain challenging due to increasing demand and limited supply. As urban areas continue to attract more residents, particularly young professionals and students, the pressure on affordable housing will persist. Government policies aimed at promoting affordable housing development may provide some relief, but the issue is likely to persist in the near future. The growing trend of remote work resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic may also impact housing preferences and demand patterns, potentially leading to shifts in the market dynamics. Overall, stakeholders in the Netherlands affordable housing market will need to innovate and collaborate to address the ongoing challenges and ensure adequate housing options for all income levels.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Outlook
- Market Size of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market, 2024
- Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market, 2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Revenues & Volume for the Period 2021-2031
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Trend Evolution
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Drivers and Challenges
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Price Trends
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Porter's Five Forces
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Industry Life Cycle
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Product Type for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Multi-Family Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Single-Family Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Modular Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Financing Type for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Government-Sponsored Programs for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Subsidized Housing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Private Financing for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By End User for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By First-time Homebuyers for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Low-Income Families for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Senior Citizens for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Veterans for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Builder Type for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Public Sector for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Private Sector for the Period 2021-2031
- Historical Data and Forecast of Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume By Mixed-Use Developments for the Period 2021-2031
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Import Export Trade Statistics
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Product Type
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Financing Type
- Market Opportunity Assessment By End User
- Market Opportunity Assessment By Builder Type
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Top Companies Market Share
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Competitive Benchmarking By Technical and Operational Parameters
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Company Profiles
- Netherlands Affordable Housing Key Strategic Recommendations
Frequently Asked Questions About the Market Study (FAQs):
1 Executive Summary |
2 Introduction |
2.1 Key Highlights of the Report |
2.2 Report Description |
2.3 Market Scope & Segmentation |
2.4 Research Methodology |
2.5 Assumptions |
3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Overview |
3.1 Netherlands Country Macro Economic Indicators |
3.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, 2021 & 2031F |
3.3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market - Industry Life Cycle |
3.4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market - Porter's Five Forces |
3.5 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Product Type, 2021 & 2031F |
3.6 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Financing Type, 2021 & 2031F |
3.7 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By End User, 2021 & 2031F |
3.8 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume Share, By Builder Type, 2021 & 2031F |
4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Dynamics |
4.1 Impact Analysis |
4.2 Market Drivers |
4.2.1 Government initiatives to increase affordable housing supply |
4.2.2 Growing population leading to increased housing demand |
4.2.3 Low interest rates making mortgages more affordable |
4.3 Market Restraints |
4.3.1 Limited availability of land for new affordable housing developments |
4.3.2 Rising construction costs impacting affordability for developers |
4.3.3 Regulatory challenges and bureaucratic hurdles slowing down housing projects |
5 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Trends |
6 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market, By Types |
6.1 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market, By Product Type |
6.1.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.1.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Product Type, 2021 - 2031F |
6.1.3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Multi-Family Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.1.4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Single-Family Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.1.5 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Modular Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market, By Financing Type |
6.2.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.2.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Government-Sponsored Programs, 2021 - 2031F |
6.2.3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Subsidized Housing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.2.4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Private Financing, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market, By End User |
6.3.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.3.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By First-time Homebuyers, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3.3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Low-Income Families, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3.4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Senior Citizens, 2021 - 2031F |
6.3.5 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Veterans, 2021 - 2031F |
6.4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market, By Builder Type |
6.4.1 Overview and Analysis |
6.4.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Public Sector, 2021 - 2031F |
6.4.3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Private Sector, 2021 - 2031F |
6.4.4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenues & Volume, By Mixed-Use Developments, 2021 - 2031F |
7 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Import-Export Trade Statistics |
7.1 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Export to Major Countries |
7.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Imports from Major Countries |
8 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Key Performance Indicators |
8.1 Average time taken for project approvals by local authorities |
8.2 Percentage of affordable housing units completed compared to set targets |
8.3 Average cost per square meter for affordable housing construction |
9 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market - Opportunity Assessment |
9.1 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By Product Type, 2021 & 2031F |
9.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By Financing Type, 2021 & 2031F |
9.3 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By End User, 2021 & 2031F |
9.4 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Opportunity Assessment, By Builder Type, 2021 & 2031F |
10 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market - Competitive Landscape |
10.1 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Revenue Share, By Companies, 2024 |
10.2 Netherlands Affordable Housing Market Competitive Benchmarking, By Operating and Technical Parameters |
11 Company Profiles |
12 Recommendations |
13 Disclaimer |
- Single User License$ 1,995
- Department License$ 2,400
- Site License$ 3,120
- Global License$ 3,795
Search
Thought Leadership and Analyst Meet
Our Clients
Related Reports
- Germany Breakfast Food Market (2026-2032) | Industry, Share, Growth, Size, Companies, Value, Analysis, Revenue, Trends, Forecast & Outlook
- Australia Briquette Market (2025-2031) | Growth, Size, Revenue, Forecast, Analysis, Trends, Value, Share, Industry & Companies
- Vietnam System Integrator Market (2025-2031) | Size, Companies, Analysis, Industry, Value, Forecast, Growth, Trends, Revenue & Share
- ASEAN and Thailand Brain Health Supplements Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- ASEAN Bearings Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Europe Flooring Market (2025-2031) | Outlook, Share, Industry, Trends, Forecast, Companies, Revenue, Size, Analysis, Growth & Value
- Saudi Arabia Manlift Market (2025-2031) | Outlook, Size, Growth, Trends, Companies, Industry, Revenue, Value, Share, Forecast & Analysis
- Uganda Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Rwanda Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
- Kenya Excavator, Crane, and Wheel Loaders Market (2025-2031) | Strategy, Consumer Insights, Analysis, Investment Trends, Opportunities, Growth, Size, Share, Industry, Revenue, Segments, Value, Segmentation, Supply, Forecast, Restraints, Outlook, Competition, Drivers, Trends, Demand, Pricing Analysis, Competitive, Strategic Insights, Companies, Challenges
Industry Events and Analyst Meet
Whitepaper
- Middle East & Africa Commercial Security Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East & Africa Fire Safety Systems & Equipment Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Drone Market Click here to view more.
- Middle East Lighting Fixture Market Click here to view more.
- GCC Physical & Perimeter Security Market Click here to view more.
6WResearch In News
- Doha a strategic location for EV manufacturing hub: IPA Qatar
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Empowering Growth: The Thriving Journey of Bangladesh’s Cable Industry
- Demand for luxury TVs surging in the GCC, says Samsung
- Video call with a traditional healer? Once unthinkable, it’s now common in South Africa
- Intelligent Buildings To Smooth GCC’s Path To Net Zero


















